Can You Water Plants With Greywater?
Understanding Greywater
Can you water plants with grey water – Greywater, a valuable resource often overlooked, represents a significant opportunity for sustainable water management. Understanding its composition, benefits, and potential risks is crucial for its safe and effective utilization in irrigation.
Greywater Definition and Sources
Greywater is wastewater generated from domestic activities excluding toilet waste. Its sources primarily include showers, bathtubs, sinks (kitchen and bathroom), and laundry machines. It’s relatively clean compared to blackwater (sewage), making it suitable for irrigation after appropriate treatment.
Greywater Composition
Typical greywater consists mainly of water, along with soaps, detergents, shampoos, food particles, hair, and skin cells. The specific composition varies depending on the source and the products used. The presence of these components necessitates filtration and treatment before use in irrigation.
Greywater vs. Wastewater
The key difference lies in the absence of fecal matter and toilet waste in greywater. Wastewater encompasses all water discharged from a home, including greywater and blackwater (sewage). Greywater, being less contaminated, presents a safer and more manageable option for reuse in irrigation compared to untreated wastewater.
Greywater Generating Activities
Several household activities contribute to greywater generation. Understanding these sources is essential for efficient greywater harvesting.
- Showers
- Bathtubs
- Bathroom sinks
- Kitchen sinks
- Laundry machines
Benefits of Greywater Irrigation: Can You Water Plants With Grey Water

Source: housedigest.com
Reusing greywater for plants is a great way to conserve water, but the type of water matters. For instance, you might wonder if the water is suitable for propagating cuttings; finding out if you can propagate a polka dot plant in water, as discussed in this helpful article can you propagate polka dot plant in water , can inform your decisions.
Ultimately, successful greywater irrigation depends on the plants’ needs and the water’s quality.
Utilizing greywater for irrigation offers numerous environmental and economic advantages, contributing to sustainable water management practices.
Environmental Advantages
Greywater irrigation significantly reduces potable water consumption, lessening the strain on municipal water supplies and preserving natural water resources. It also minimizes the amount of wastewater entering sewage treatment plants, reducing the environmental impact of treatment processes.
Water Conservation
By diverting greywater away from the sewage system and towards irrigation, substantial water savings are achieved. This is particularly beneficial in water-scarce regions or during periods of drought.
Cost-Effectiveness
Greywater irrigation systems, while requiring initial investment, offer long-term cost savings by reducing reliance on municipal water supplies. The reduced water bills can offset the initial investment costs over time.
Successful Greywater Irrigation Examples
Successful greywater irrigation systems have been implemented across various climates, demonstrating their adaptability and effectiveness.
| Climate | System Type | Plant Types | Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mediterranean (California) | Drip irrigation | Ornamental shrubs, fruit trees | Significant water savings, healthy plant growth |
| Arid (Arizona) | Subsurface irrigation | Cactus, succulents | Reduced water usage, minimal evaporation |
| Temperate (Oregon) | Above-ground system | Vegetables, flowers | Successful irrigation, minimal maintenance |
| Subtropical (Florida) | Combination system (drip and subsurface) | Tropical plants, palms | Efficient water distribution, lush growth |
Risks and Precautions of Greywater Irrigation
While offering numerous benefits, greywater irrigation requires careful consideration of potential risks and implementation of appropriate safety measures.
Potential Risks of Untreated Greywater
Untreated greywater can contain pathogens and contaminants that may harm plants or pose health risks if improperly handled. These include bacteria, viruses, and soap residues that can affect soil health and plant growth.
Importance of Filtration and Treatment
Effective filtration and treatment are crucial to remove harmful contaminants from greywater before use in irrigation. This minimizes the risk of disease transmission and maintains soil health.
Safe Greywater Storage and Distribution
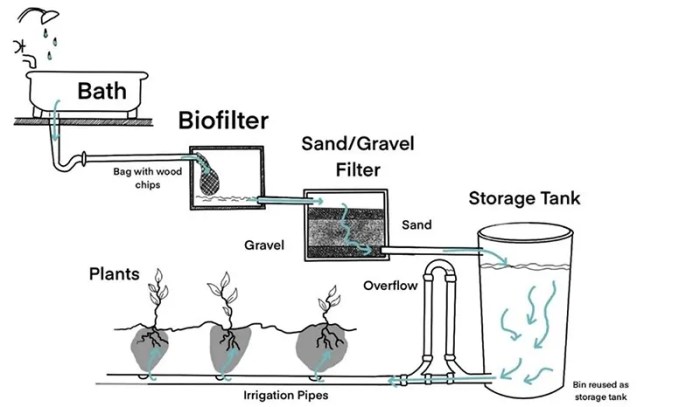
Source: kxcdn.com
Proper storage and distribution methods prevent contamination and ensure safe handling. This includes using appropriate containers, avoiding stagnant water, and employing suitable distribution systems.
Health Concerns and Preventative Measures
Improper greywater handling can lead to health issues. Preventative measures include wearing protective gloves during handling, avoiding direct contact with untreated greywater, and ensuring proper system maintenance to prevent leaks and spills.
Suitable Plants for Greywater Irrigation
Certain plant species demonstrate greater tolerance to the components found in greywater, making them ideal choices for greywater irrigation systems.
Plants Tolerant of Greywater
A variety of plants thrive when irrigated with greywater. Selecting appropriate species ensures successful irrigation and minimizes potential risks.
- Lavender
- Rosemary
- Eucalyptus
- Oleander
- Aloe Vera
Detailed Plant Descriptions
Five plant species suitable for greywater irrigation, along with their water requirements and tolerance levels, are described below. These descriptions provide a guide for selecting plants based on specific conditions.
- Lavender: Prefers well-drained soil and tolerates drought conditions. Greywater irrigation can supplement its water needs, promoting healthy growth.
- Rosemary: A drought-tolerant herb that thrives in sunny locations. Greywater irrigation can provide supplementary moisture, enhancing its flavor and fragrance.
- Eucalyptus: A fast-growing tree with high water requirements. Greywater can be a sustainable irrigation source, supporting its growth in suitable climates.
- Oleander: A drought-tolerant shrub that tolerates salty conditions. Greywater irrigation can be effectively used, minimizing the need for potable water.
- Aloe Vera: A succulent that requires infrequent watering. Greywater can be used sparingly to supplement its moisture needs.
Greywater vs. Potable Water Growth Comparison
Comparative studies have shown that many plants exhibit similar growth rates when watered with properly treated greywater versus potable water. In some cases, greywater can even enhance growth due to the nutrient content.
Small Garden Plan for Greywater Irrigation
A small garden plan incorporating a drip irrigation system and utilizing drought-tolerant plants such as lavender, rosemary, and succulents would be suitable for greywater irrigation. Plants should be spaced appropriately to allow for adequate sunlight and airflow.
Designing a Greywater Irrigation System
Several design options exist for greywater irrigation systems, each tailored to specific needs and conditions.
Greywater Irrigation System Designs
Various designs cater to different needs and scales, from simple drip systems to more complex subsurface installations.
- Drip irrigation: Delivers water directly to plant roots, minimizing water waste.
- Subsurface irrigation: Distributes water underground, reducing evaporation and weed growth.
- Above-ground systems: Simple to construct but more prone to evaporation and weed growth.
Components of a Basic System
A basic greywater system typically includes a collection tank, filter, pump, and distribution pipes. The specific components may vary based on system design and scale.
Constructing a Simple Greywater System
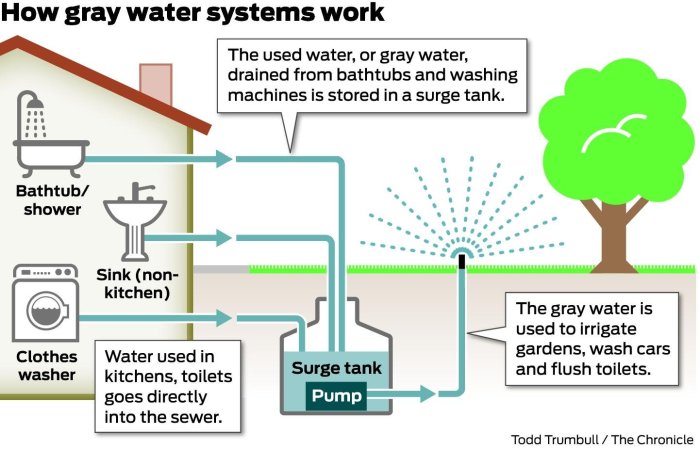
Source: hdnux.com
Building a simple greywater system involves several steps, from collection to distribution. Careful planning and execution are essential for a functional and safe system.
-
Collect greywater from appropriate sources (showers, sinks, laundry).
-
Filter the greywater to remove solids and debris.
-
Store the filtered greywater in a suitable container.
-
Install a pump to distribute the greywater to the irrigation system.
-
Use drip irrigation or other suitable methods to deliver water to plants.
Illustrative Examples of Greywater Systems
Greywater systems can be adapted for various scales and settings, from small residential gardens to larger community projects.
Residential Greywater System, Can you water plants with grey water
Imagine a system in a small home where greywater from the shower and bathroom sink is collected in an underground tank. A simple filter removes larger debris. A small pump, activated by a timer, distributes the water through a network of drip lines leading to potted plants and a small vegetable patch. The tank is visually unobtrusive, perhaps located under a shed, and the system’s operation is largely automated, requiring minimal maintenance.
Large-Scale Greywater System
Envision a community garden utilizing a larger-scale greywater system. Greywater from multiple households is collected via a network of pipes and directed to a central filtration and storage facility. The system employs a more robust filtration process, perhaps including UV sterilization. Water is then distributed through a network of subsurface irrigation lines spanning the entire garden. The central facility might include monitoring equipment and a control panel, while the garden itself showcases a thriving array of diverse plants irrigated sustainably with the recycled water.
FAQ Compilation
Can I use greywater from the toilet?
No, greywater does not include wastewater from toilets. Toilet water contains harmful bacteria and pathogens unsuitable for plant irrigation.
How often should I filter my greywater?
The frequency of filtering depends on your system and the type of filter used. Consult your system’s instructions for specific recommendations.
What if I don’t have space for a large greywater system?
Even small-scale systems can be effective. A simple bucket system with a filter can be used for a few plants.
Are there any legal restrictions on greywater irrigation?
Regulations vary by location. Check with your local authorities before implementing a greywater system.




















